By Mohamed Tawfek Elkhishin and Malik Altaf Hussain department of Wine, Food and Molecular Biosciences, Lincoln University
The most widely accepted definition of probiotics describes them as live micro-organisms, which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit to the host/human.
The list of beneficial health effects for people who use the probiotic food products continues to expand. The stated benefits of probiotics consumption that are frequently mentioned include:
- Immune system stimulation
- Improvement of the digestive processes
- Enhanced resistance to toxic bowel disease and diarrhoea
- Decrease of cholesterol level in blood serum
- Reduction in toxic metabolism by gut microflora
Nowadays, probiotic food products are becoming increasingly popular and their market is growing worldwide. The most common commercially available probiotic products are fermented dairy products like buttermilk, yoghurt and sour cream.
Recent technological developments have made it possible to incorporate and deliver probiotics using non-dairy based food products. New probiotic products in the market as well as novel concepts in the research publications are expanding rapidly.
There are several drivers for the expansion of markets for new probiotic food products. One of the most important is the increased demand for non-dairy based probiotic food products. Moreover, the size of the probiotics market has increased sharply in the last few years and the predicted value of the European market for probiotics is 120 million by 2013. A similar trend in the popularity of probiotics products is seen New Zealand.
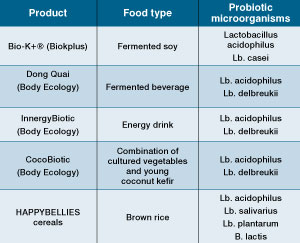
To fulfil this global ambition many newly developed probiotic food products (Table 1) are now available. Some of them are very interesting and novel.
Fermented soy probiotic product (Bio-K+)
A soybean based probiotic product (Bio- K+(r)) was introduced by a company called BioKplus. Soy or soy products are an important part of the Asian diet and fermented soy products are acceptable and commonly consumed. In fact, the process of fermentation is useful for increasing the digestibility of soy products.
Brown rice cereal (HAPPYBELLIES cereals)
Brown rice cereal is a product designed for babies to provide plenty of “good bowel bugs”. Probiotic fermented rice can be another substitute to dairy products and rice bran can be used as an alternative source for non-dairy probiotics. This product contains fibre (prebiotic) that can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria (Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species).
CocoBiotic (Body ecology)
CocoBiotic is a naturally-fermented drink made from green coconuts and natural probiotic kefir to improve digestion and to increase the function of the immune system.
Dong Quai (Body Ecology)
‘Dong Quai’ is the Chinese name for the herb Angelica polymorpha, also known as “women’s ginseng” for its role in balancing female hormones and the female reproductive cycle. A fermented probiotic beverage containing ‘Dong Quai’ is available in the market that claims to maintain proper digestion and immune function, and promote nourishing and cleansing of the blood (http://bodyecology.com/probiotic-drink-dong-quai.html).
Technological developments along with high productivity procedures are helping the scientific community to create novel probiotic products. These developments are providing vital information to identify the benefits of the probiotic microbes, and characterise the robustness of these microorganisms, which are the key to the innovative application of probiotics by creating novel food product ideas. A number of examples can be quoted from published research.
- Development of functional meat products is a growing area of research
- Dried probiotics can have a longer shelf life than liquid products as well as being more convenient to handle and transport
The increasing demand for probiotics and the probiotic food products challenges the food industry to develop innovative product ranges to satisfy the tastes of consumers in newly emerging markets. A new generation of probiotic food products will take a prominent place and replace traditional dairy-based probiotic products. Finally, there are novel products arising from on-going research activities to target specific market needs or groups of consumers.
Dr Malik Hussain is a lecturer in food microbiology at Lincoln University. Research on probiotics is a major component of the activities at Food Microbiology laboratory (the Department of Wine, Food and Molecular Bioscience). If you are interested in probiotics research, Email [email protected]